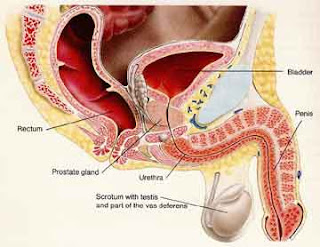
 Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is an enlarged prostate gland. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. As the prostate gets bigger, it may squeeze or partly block the urethra. This often causes problems with urinating.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is an enlarged prostate gland. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. As the prostate gets bigger, it may squeeze or partly block the urethra. This often causes problems with urinating.Benign prostatic hyperplasia is probably a normal part of the aging process in men, caused by changes in hormone balance and in cell growth.
Prostate enlargement is very common as men age -- symptoms usually develop around age 50 and by age 60, most men have some degree of BPH. At age 85, men have a 90% chance of having urination problems caused by BPH. It' s important to note that BPH is not cancer, and it does not put you at increased risk for developing prostate cancer.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia Pre-Surgery Care
Assess the client's anxiety, correcting misconceptions about the surgery and provide accurate information on the client:
- Type of surgery
- Type of anesthetics
- Cateter: Foley catheter, Continuous Bladder Irigation (CBI).
Pre-Surgery Preparation others are:
- Complete laboratory examination.
- Examination of the ECG
- Examination of Radiology.
- Examination Uroflowmetry: For people who do not wear a catheter.
- Installation of infusion and fasting.
- Shaving pubic hair and lavement.
- Giving antibiotics.
- Approval of Operations (Informed Concern).
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - Post-Surgery Care
Post-Surgery Care is basically the same as for other patients, namely: monitoring of respiration, circulation and awareness of the patient:
1. Monitoring of respiration
- Airway: Clear the airway, the position of the head of extensions
- Breathing: Provide oxygen as needed, observation of respiratory
- Circulation: measuring blood pressure, pulse, body temperature, breathing, awareness and urine production in the early phase (6 hours) post-operative must be monitored every hour and should be recorded.
- When the initial phase is stable, monitor / interval can be 3 hours.
- When blood pressure drops, pulse increases (small), dark red urine production should be wary of bleeding: Hb checks immediately and inform doctors.
- Tensions increased and decreased pulse (bradycardia), decreased potassium levels, anxiety or delirium should be wary: immediately report the doctor.
- If urine output decreased / not out, looking for the cause is clogged by a blood clot catheter, urinary retention occur in the bladder: report physician,
- If necessary checks blood gas analysis
- Is there pallor, bluish.
- Check lab: Hb, RFT, Na / K and a urine culture.
2. Giving Antibiotics
3. Catheter care
Urethral catheter that is placed on postoperative prostate, namely folley 3 hole catheter (Catheter Tree Way), size 24 Fr.
The three holes are useless:
- To fill the balloon, between 30-40 ml of fluid.
- To undertake irrigation / spoling.
- To discharge (urine and fluid spoling).